The prostate is a small gland which is located at the base of the urinary bladder in men. With advancing age the prostate can enlarge (called as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia or BPH). BPH affects more than 50% of men by the age of 60 years and up to 80% of men older than 70 years, and its prevalence is increasing as the population ages.
Enlarged prostate (BPH) leads to symptoms such as urinary frequency, urgency, nocturia, weak stream, dribbling and Chronic urinary retention. These symptoms can greatly affect the quality of life of a person.
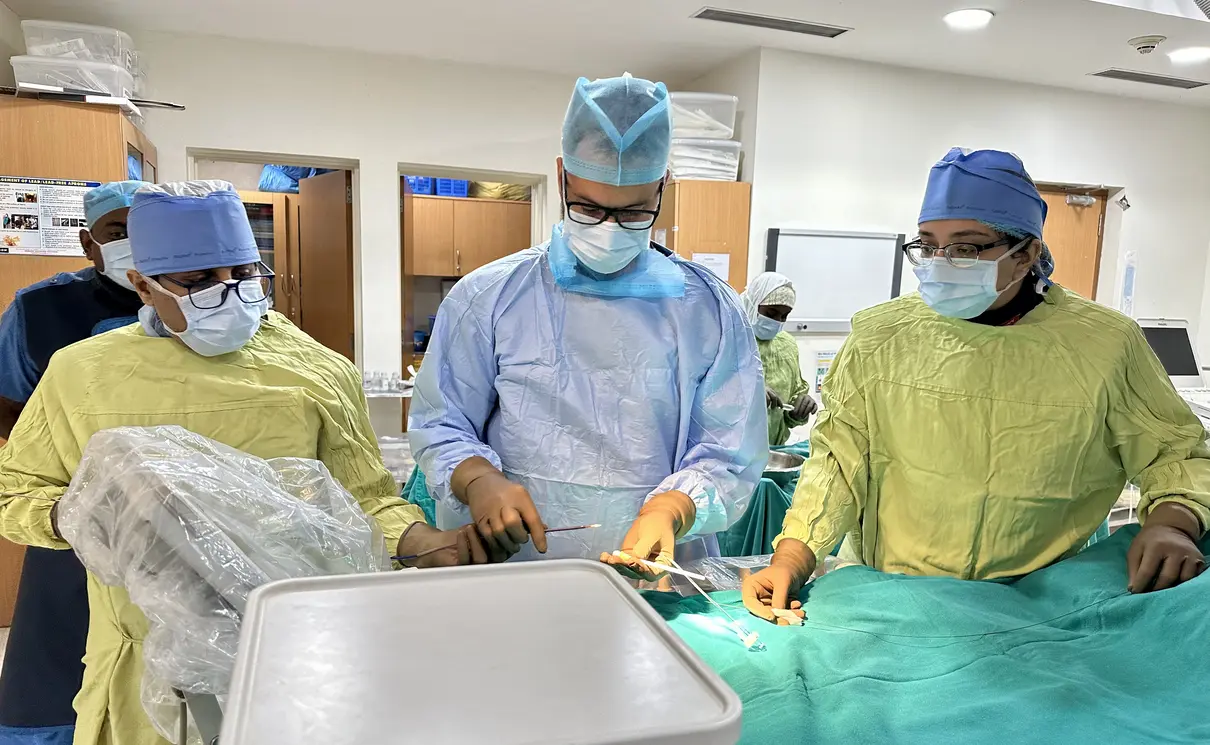
Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) is a cutting-edge procedure that can provide relief for this problem.
FAQs
1. How does Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) work?
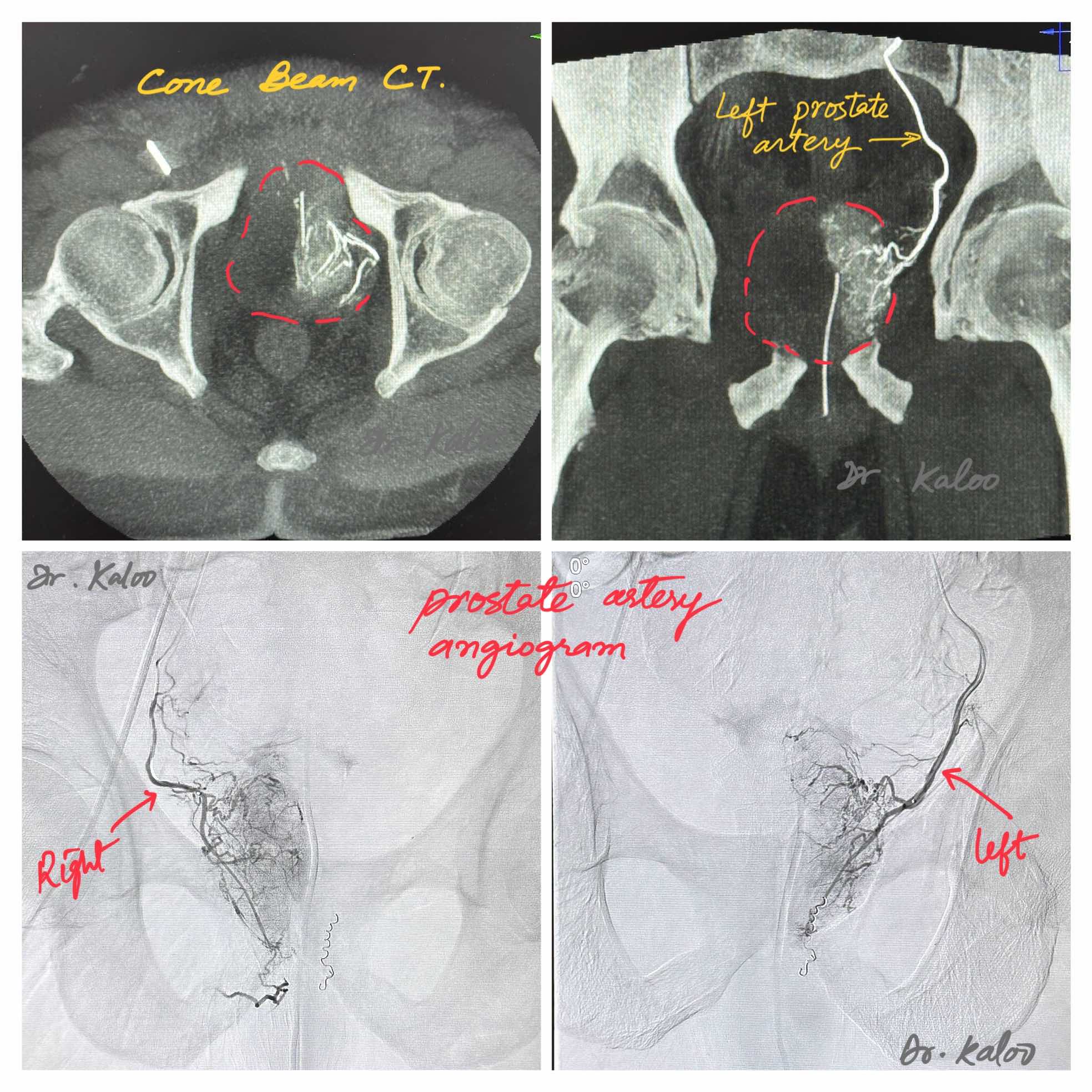
A. PAE procedure is done in an angiography suite. Medical imaging is used to guide a tiny catheter into the arteries that supply blood to the prostate. Once in place, tiny particles are injected through the catheter that block these arteries, thus reducing blood flow to the prostate. This reduction in blood flow causes the prostate to shrink, providing relief to the patient.
2. What are the benefits of PAE?
A. One of the main benefits of PAE is that it's minimally invasive. It does not require surgery or general anaesthesia. Recovery is usually quick and most patients can go home within a day. Over next few days and weeks, the prostate shrinks in size and patients experience significant improvement in their symptoms.
The other advantages of PAE are:
- Preserves sexual function.
- Shorter recovery time compared to surgery.
- Reduced risk of complications.
PAE is thus an excellent treatment option for men with prostate enlargement. If you are experiencing symptoms related to an enlarged prostate, reach out to an interventional radiologist to discuss whether PAE is right for you. Your quality of life matters, and PAE could be the solution you've been looking for.